Advancing our understanding Developing better ways to treat disease

How does the normal brain function?
How do we use that knowledge to fix the brain in disease?
Fostering an environment for discovery

Solving the puzzles of the brain takes all of our brains
Mission
The mission of Scharfman Lab research is to advance our understanding of the healthy brain and use that information to help 'fix' the brain when it is not functioning correctly.
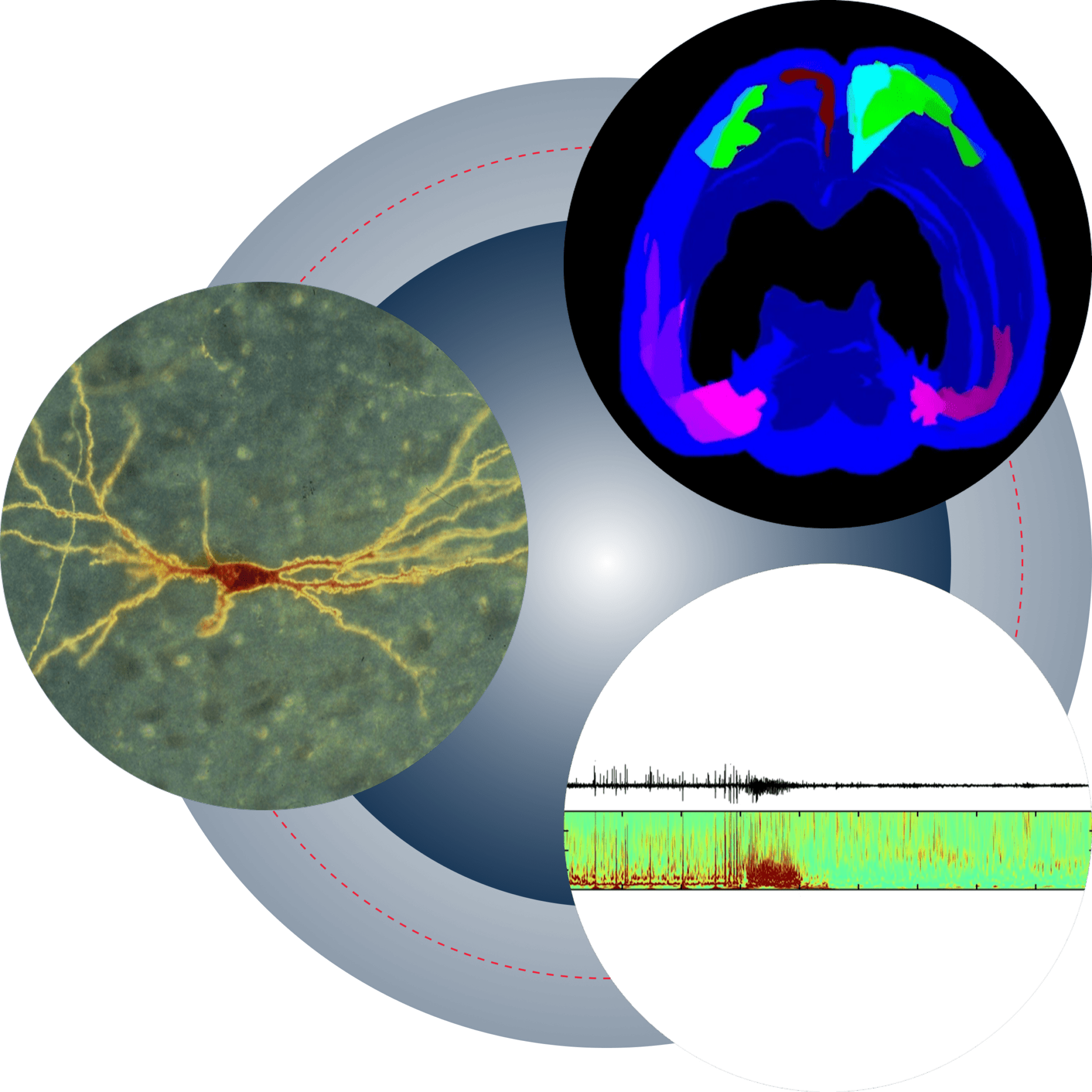
We study the hippocampus, an area of the brain that plays a critical role in memory and emotions. A healthy hippocampus has an inherent capacity to change or be 'plastic,' meaning that it can form new memories and modify emotions. Unfortunately, damage to the hippocampus occurs in many neurological diseases, such as epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease.
Advancing Disease Research with Animal Models
Our laboratory mainly uses rats and mice that simulate what occurs in humans, so-called animal models of disease. Some of these models involve a mutation that is found in humans, such as in some types of Alzheimer's disease. Other models involve an initial treatment of a normal animal that leads to some characteristics of the disease, such as seizures in epilepsy. Our goals are to devise treatments in these animal models that could ultimately treat humans.
Finally, our mission is to promote science that has integrity and rigor, treats all individuals with respect, and provides a role for everyone in the lab, no matter their stage of training.
Exploring Brain Plasticity and Neurogenesis
We are interested in the mechanisms underlying plasticity, such as the ability of the brain to make modifications to neuronal structure (axons, spines), synaptic strength (long-term potentiation and depression), and the ability to generate action potentials (excitability). As a result, we are also interested in a number of trophic or growth factors such as neurotrophins (BDNF), hormones (estrogen, androgen), and mechanisms that control excitability.
Within the hippocampus, we focus on the dentate gyrus, an area of the brain that has unique attributes. One is the capacity to generate neurons throughout adulthood, called adult neurogenesis. Another is a cell type called a mossy cell, which appears to regulate adult neurogenesis, memory, emotions, and excitability. Mossy cells also appear to contribute to epilepsy and possibly Alzheimer's disease.
Life in The Lab
The best lab
Giving Helen flowers after her receipt of the Research Recognition Award from the American Epilepsy Society.
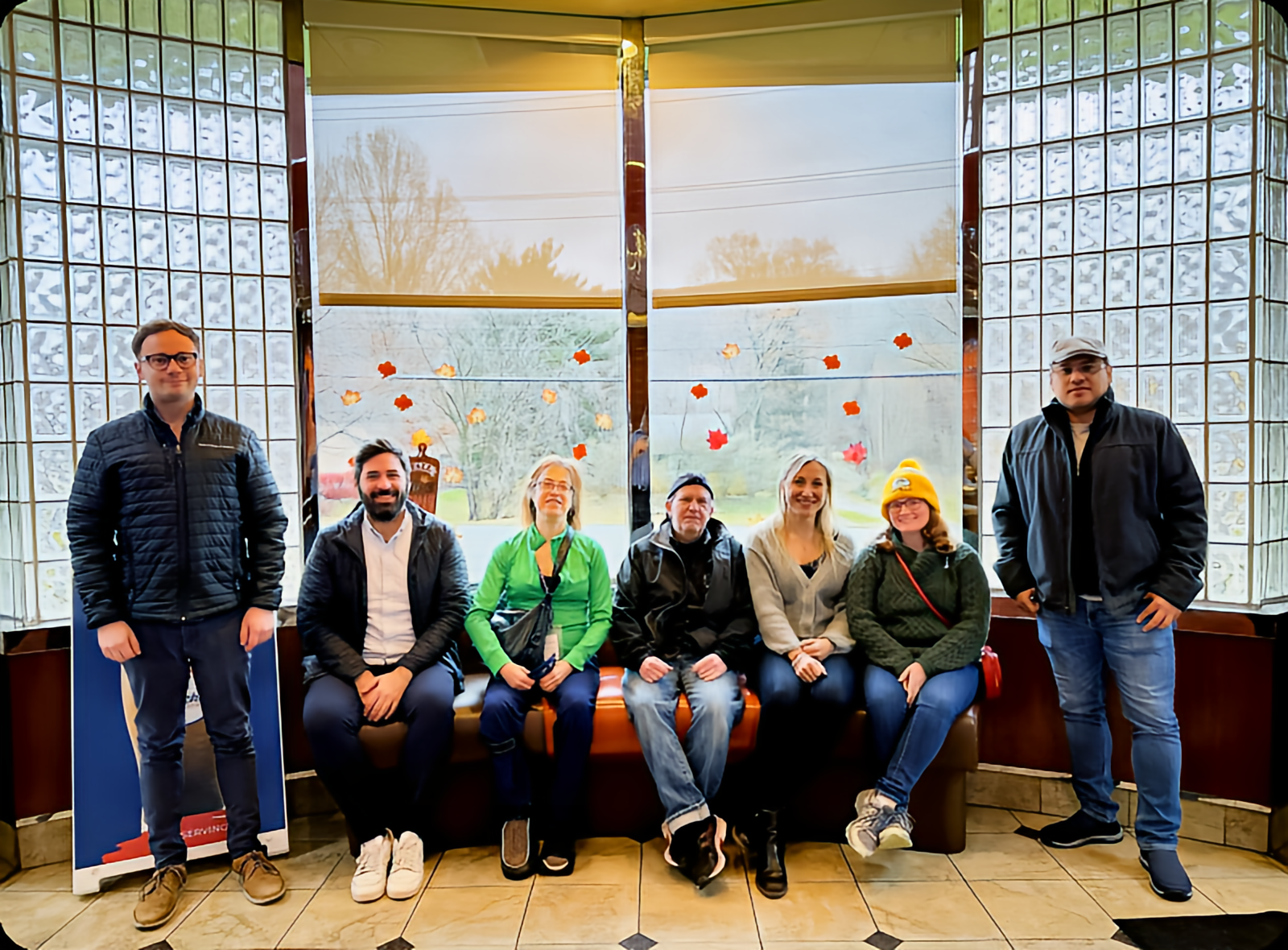

The lab in 2023
Smiles after a Thanksgiving lunch. From left to right: Gabriel Stephens, Christos Lisgaras, Helen Scharfman, John LaFrancois, Chiara Criscuolo, Meghan Kennedy, and David Alcantara-Gonzalez.
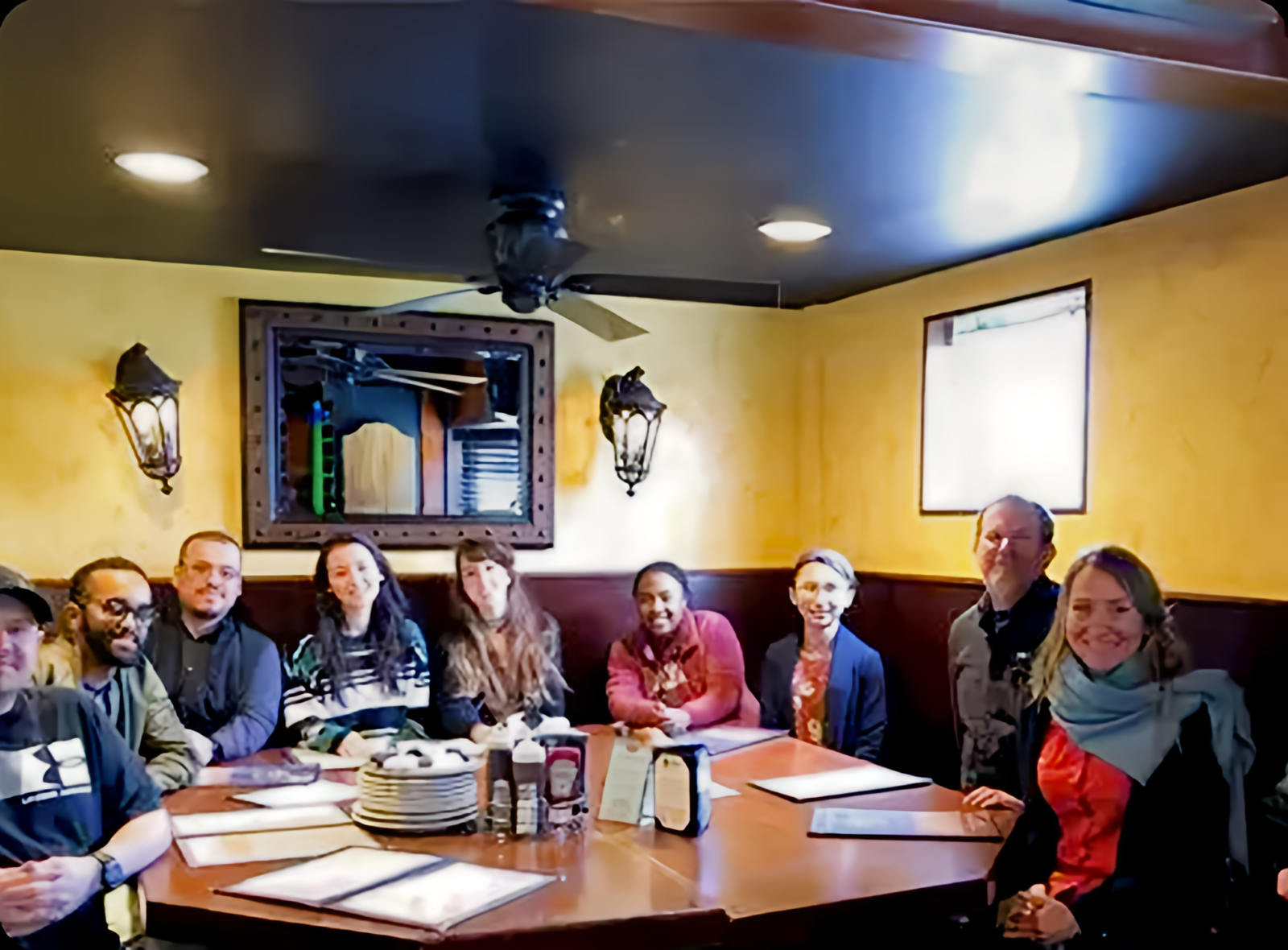

Past and Present Lab Members
Another lab lunch, this one several years ago. From left to right: Justin Botterill, Kndeya Gebrewahed, David Alcantara-Gonzalez, Liza Chartampila, Kasey Gerencer, Nia Boles, Yi-Ling Lu, John LaFrancois, Chiara Criscuolo, and Helen Scharfman.